Decentralized Autonomy: Unpacking The Enigmatic World Of DAOs
Decentralized Autonomy: Unpacking the Enigmatic World of DAOs
- The Rise Of Decentralized Exchanges: Revolutionizing The Crypto Trading Landscape
- Navigating The Wild West Of Crypto Trading: A Beginner’s Guide To Safe Trading With Stop Loss Orders
- Dive Into The World Of Decentralized Finance With Yield Farming
- The Future Of Online Commerce: How Crypto Is Poised To Revolutionize The Way We Shop
- Unveiling The Power Of Zero Knowledge Proofs In Protecting Your Cryptographic Identity
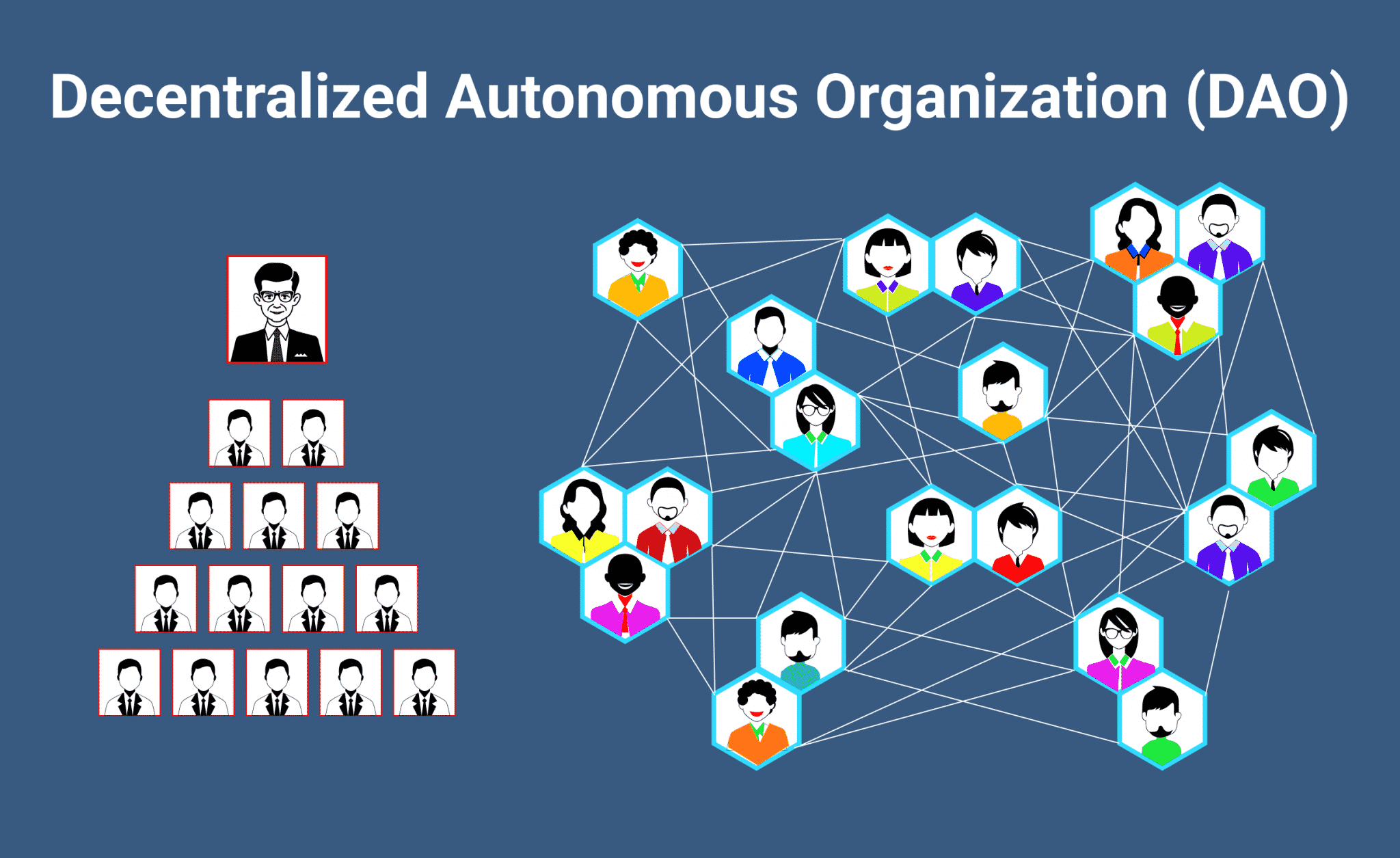
Imagine a world where decision-making is distributed, transparent, and community-driven. A realm where the traditional hierarchies of power are upended, and every participant has an equal say in shaping the future. Welcome to the world of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, or DAOs for short.
At its core, a DAO is an organization that operates on a blockchain network, governed by a set of rules encoded in smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automate the decision-making process, ensuring that the organization’s activities are transparent, secure, and free from centralized control.
In a traditional organization, decision-making is typically top-down, with a select few calling the shots. In contrast, a DAO flips this script by distributing power among its members. By tokenizing participation, DAOs enable anyone to contribute to the decision-making process, provided they hold the required tokens.
So, how do DAOs operate? The process can be broken down into several key components:
- Token distribution: Members acquire tokens, which serve as proof of ownership and participation in the DAO. These tokens can be bought, sold, or exchanged on cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Proposal creation: Members submit proposals for the DAO, outlining the changes they want to implement or the decisions they want to make. Proposals can range from simple changes to more complex decisions, such as adjusting the DAO’s budget or selecting new members.
- Voting: Once a proposal is submitted, it’s put to a vote by the DAO’s members. Each member’s tokens are used to cast votes, with the weight of their vote determined by the number of tokens they hold. The outcome of the vote determines whether the proposal is accepted or rejected.
- Execution: If a proposal is approved, the DAO’s smart contracts execute the changes automatically, ensuring that the organization’s funds and assets are distributed accordingly.
DAOs have many potential applications, from:
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): DAOs can govern the flow of funds, manage risk, and make decisions on investments and lending.
- Social organizations: DAOs can facilitate community-driven decision-making for non-profit organizations, cooperatives, and social movements.
- Innovation: DAOs can facilitate open-source innovation, allowing developers to collaborate on new projects and products.
However, DAOs are still in their infancy, and the technology is still evolving. Challenges such as scalability, security, and regulatory compliance need to be addressed before DAOs can reach their full potential.
Despite these challenges, the potential of DAOs to democratize decision-making and create more inclusive, transparent organizations is undeniable. As the world grapples with the complexities of technological advancements, DAOs offer a glimpse into a future where power is truly decentralized and participatory.
In this brave new world, DAOs are poised to revolutionize the way we think about governance, decision-making, and the distribution of power. As we continue to navigate this uncharted territory, one thing is clear: the future is decentralizing, and DAOs are at the forefront of this revolution.
