The Blockchain Puzzle: Unraveling The Complexity Of Layer 1 And Layer 2 Solutions
The Blockchain Puzzle: Unraveling the Complexity of Layer 1 and Layer 2 Solutions
- Staying One Step Ahead Of The Crypto Scammers: Expert Tips To Protect Your Digital Assets
- Navigating The World Of Crypto: Top Exchanges For Beginners
- Breaking Down Barriers In The Blockchain World: Interoperability Protocols
- Secure Your Crypto Fortune: Expert-Recommended Cold Wallets For 2024
- Navigating Turbulent Tides: Strategies For Safeguarding Your Crypto Investments
Imagine a bustling city with a complex network of roads, highways, and public transportation systems. This is similar to the world of blockchain, where a multitude of layers and solutions work together to create a seamless and efficient experience. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of blockchain complexity, focusing on layer 1 and layer 2 solutions that underpin the entire ecosystem.
The Blockchain Basics: A Quick Refresher
Before we dive into the complexities, let’s quickly revisit the basics. Blockchain technology is a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It’s the foundation for cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and a multitude of other applications. However, as the popularity of blockchain grows, so does the complexity of its architecture.
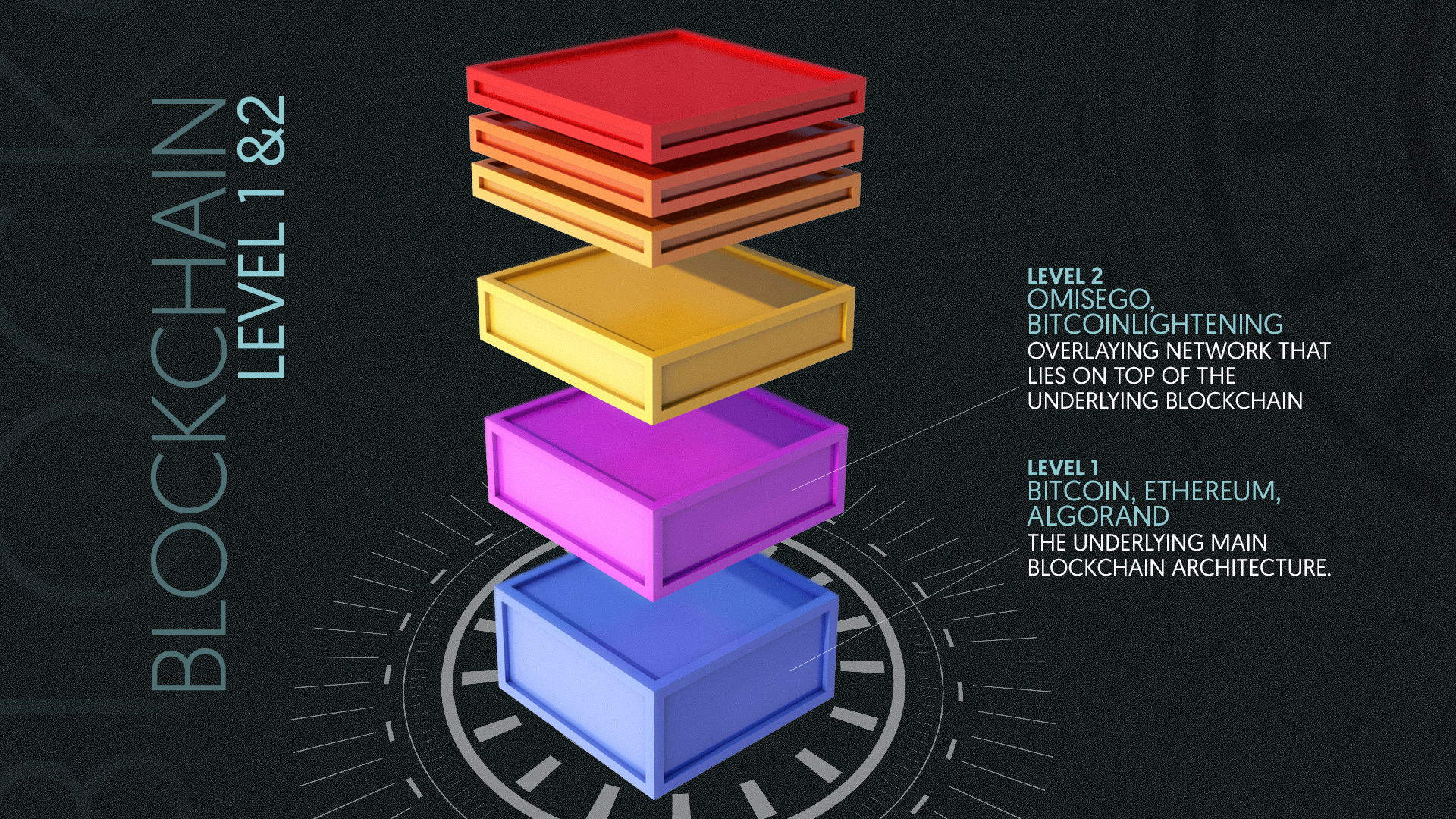
Layer 1: The Foundation
Layer 1 refers to the underlying protocol of a blockchain, which includes the consensus algorithm, network architecture, and smart contract functionality. In other words, layer 1 is the fundamental framework that enables transactions to occur on the blockchain. Think of it as the city’s roads and highways, providing the basic infrastructure for movement.
Some notable examples of layer 1 blockchains include:
- Bitcoin (BTC)
- Ethereum (ETH)
- Polkadot (DOT)
- Solana (SOL)
Each layer 1 blockchain has its unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations. For instance, Bitcoin is optimized for security and decentralization, while Ethereum is more focused on smart contract functionality.
The Limitations of Layer 1
While layer 1 blockchains provide a solid foundation, they often face challenges related to scalability, usability, and transaction efficiency. As the network grows, so does the complexity, leading to:
- Increased transaction fees
- Decreased transaction speed
- Limited scalability
- High energy consumption
These limitations hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain technology, which is where layer 2 solutions come into play.
Layer 2: The Efficiency Boosters
Layer 2 solutions are designed to alleviate the scalability and usability issues faced by layer 1 blockchains. They operate on top of the existing layer 1 architecture, providing additional functionality, and optimizing transaction processing. Think of layer 2 solutions as the public transportation systems and optimized traffic management of our city analogy.
There are several types of layer 2 solutions, including:
- State channels: enable multiple transactions to be processed off-chain, reducing network congestion and fees. (e.g., Lightning Network for Bitcoin)
- Rollups: aggregate transactions into a single batch, reducing the load on the layer 1 blockchain. (e.g., Optimism for Ethereum)
- Sidechains: separate blockchains that operate in parallel, allowing for faster transaction processing and lower fees. (e.g., Polkadot’s interoperability framework)
