The Role Of Blockchain In Decentralized Energy Grids
Imagine a world where energy is not controlled by a single entity, but rather by the people who use it. A world where renewable energy sources are harnessed to their full potential, and energy transactions are transparent, secure, and efficient. Welcome to the world of decentralized energy grids, powered by blockchain technology.
- The Impact Of Decentralized Finance Defi On Traditional Banks
- The Best Crypto Debit Cards For 2024
- What Are Crypto Derivatives And How Can You Trade Them
- The Evolution Of Trading Unpacking The Differences Between Centralized And Decentralized Exchanges
- The Harmony Of Blockchain And Music: Unlocking The Future Of The Industry
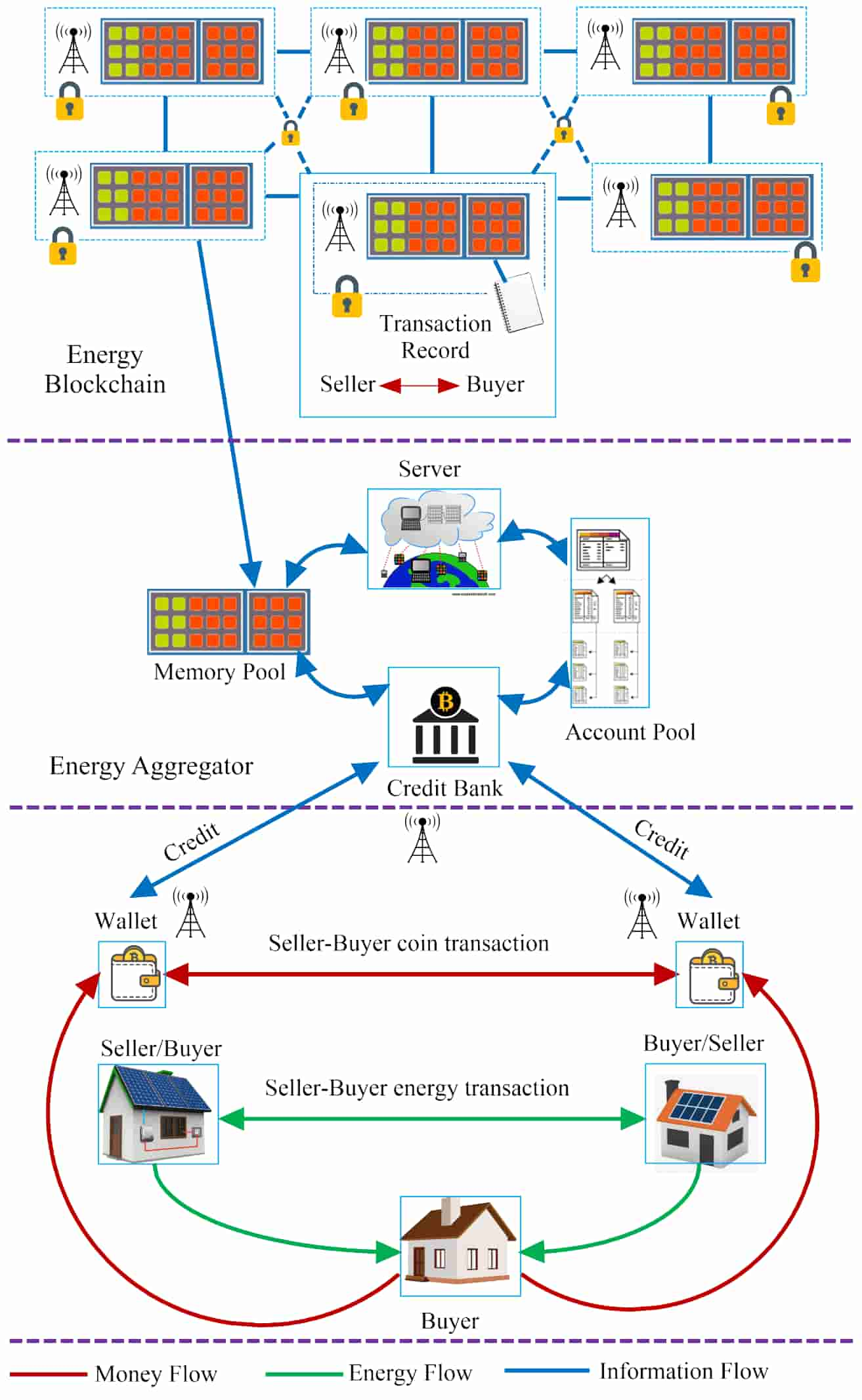
In traditional energy grids, energy is generated, transmitted, and distributed by a centralized authority. This approach has several drawbacks, including high energy losses, lack of transparency, and limited access to renewable energy sources. However, with the advent of blockchain technology, the energy landscape is shifting towards a decentralized, democratized, and decarbonized future.
Blockchain, the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has been gaining traction in various industries, including energy. In the context of energy grids, blockchain enables the creation of a decentralized network, where energy is generated, stored, and traded by multiple stakeholders. This peer-to-peer network allows for direct transactions between consumers, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing energy efficiency.
One of the key benefits of blockchain in decentralized energy grids is the promotion of renewable energy sources. Traditional energy grids are designed to rely on centralized power plants, which often run on fossil fuels. In contrast, decentralized energy grids encourage the adoption of rooftop solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy sources. Blockchain technology enables these sources to be integrated into the grid, providing a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix.
Another advantage of blockchain in energy grids is its potential to increase energy security. In traditional grids, energy is vulnerable to cyber attacks, which can lead to power outages and economic losses. Blockchain’s decentralized and encrypted nature makes it a secure platform for energy transactions, reducing the risk of cyber attacks and ensuring a more resilient energy grid.
Blockchain also enables the creation of new business models in the energy sector. For example, peer-to-peer energy trading allows consumers to sell excess energy to their neighbors, promoting a culture of sharing and collaboration. Additionally, blockchain-based platforms enable companies to offer energy storage and energy-as-a-service solutions, providing consumers with more flexibility and control over their energy usage.
One of the most promising applications of blockchain in energy grids is the development of smart grids. Smart grids use advanced technologies, including blockchain, to manage energy distribution and consumption in real-time. These grids can detect changes in energy demand and adjust supply accordingly, reducing energy waste and improving overall efficiency.
While the potential of blockchain in decentralized energy grids is vast, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. For example, the scalability of blockchain technology is still a concern, as the number of transactions per second is limited. Additionally, regulatory frameworks need to be developed to support the adoption of blockchain in energy grids.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain in decentralized energy grids looks bright. As the world continues to shift towards a low-carbon economy, the need for decentralized, democratized, and decarbonized energy systems will only increase. Blockchain technology has the potential to play a key role in this transition, enabling a more efficient, sustainable, and secure energy future.
In the not-too-distant future, we can expect to see blockchain-powered energy grids that are resilient, adaptive, and responsive to changing energy needs. These grids will be powered by a combination of renewable energy sources, energy storage, and advanced technologies, including blockchain. As we embark on this journey towards a decentralized energy future, one thing is clear: blockchain technology will be a key enabler of a more sustainable, secure, and efficient energy grid.
