Understanding The Backbone Of Blockchain Security
In recent years, the term ‘blockchain’ has become synonymous with ‘security’. But have you ever stopped to think about what really makes this technology so secure? Is it the use of cryptography, the decentralized nature of the network, or something else entirely?
- Protecting Your Digital Gold: A Comprehensive Guide To Safely Storing Your Cryptocurrency Wallets
- The Role Of Blockchain In Decentralized Voting Systems
- The Rise Of Decentralized Platforms In Shaping The Gig Economys Future
- Unlocking Economic Opportunities In Emerging Markets With Crypto
- Cracking The Crypto Code: Uncovering The Next Big Gem
To answer this question, we need to take a step back and look at the core components that underpin blockchain security. In this article, we’ll delve into the nuts and bolts of blockchain cryptography and explore the ways in which it provides a secure foundation for this technology.
Table of Content
Understanding Hash Functions
Hash functions are the building blocks of blockchain security. A hash function is a mathematical algorithm that takes input data of any size and produces a fixed-size output, known as a ‘hash’. This hash is a digital fingerprint that represents the input data.
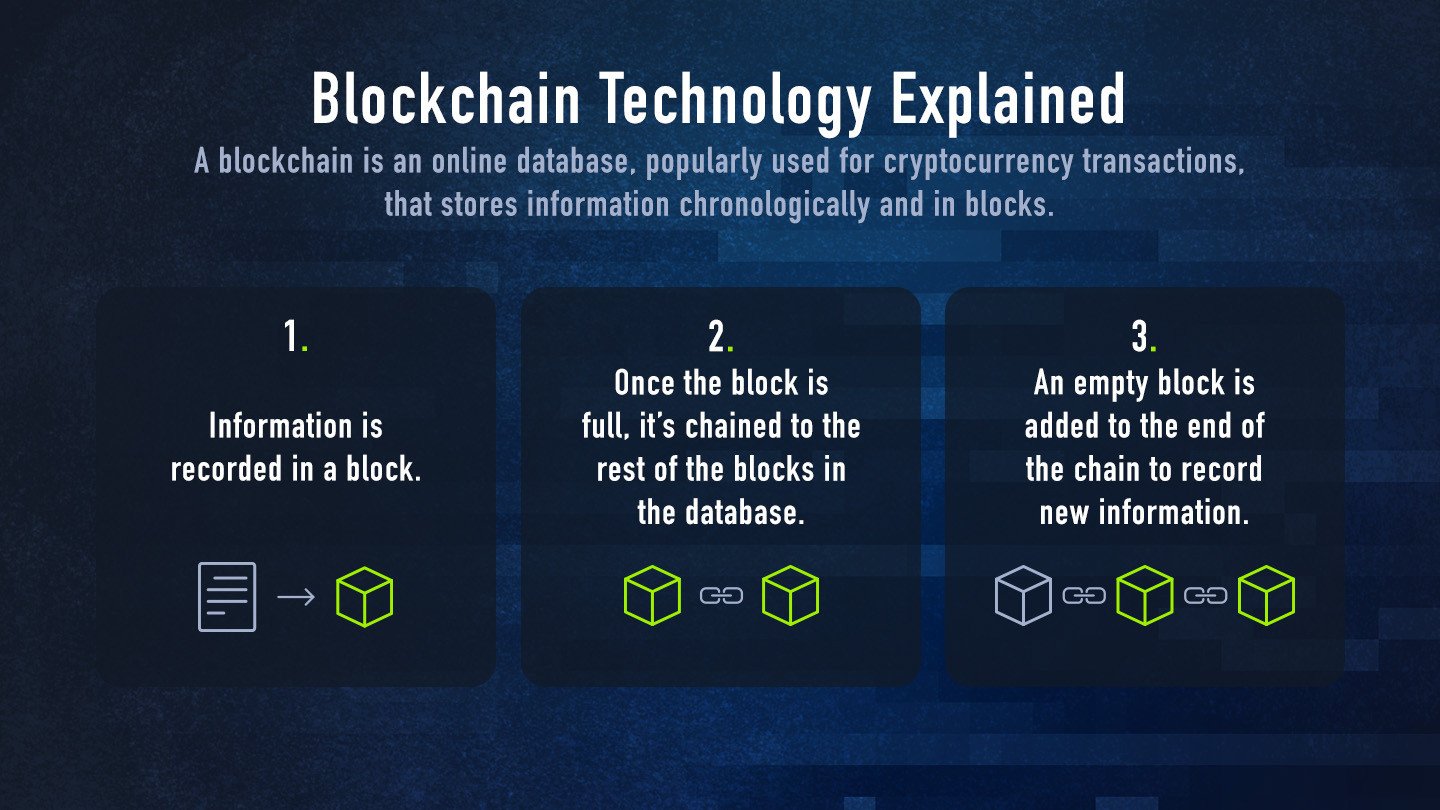
In blockchain, hash functions are used to create a digital chain of blocks, where each block contains a hash of the previous block. This creates a permanent and unalterable record of all transactions that have taken place on the network.
For example, let’s say that Alice sends 10 units of cryptocurrency to Bob. The transaction is verified by a network of nodes, and then combined with other transactions in a batch called a ‘block’. A hash function is applied to this block, creating a unique digital fingerprint. This fingerprint is then broadcast to the network, where it’s verified by nodes and added to the blockchain.
The beauty of hash functions lies in their ability to be deterministic. This means that given a specific input, the output will always be the same. This makes it virtually impossible for an attacker to alter the input data without changing the output hash.
Complementing Hash Functions with Digital Signatures
While hash functions provide a solid foundation for blockchain security, they’re not enough on their own. That’s where digital signatures come in. A digital signature is a cryptographic technique that allows a user to prove ownership of a private key, without revealing the key itself.
In blockchain, digital signatures are used to validate transactions. When a user wants to make a transaction, they create a message with the transaction details and sign it with their private key. The signed message is then broadcast to the network, where it’s verified by nodes using the user’s public key.
The public key is like a unique identifier that corresponds to the user’s private key. When a node verifies a digital signature, it checks that the signature was created using the user’s private key. This ensures that the transaction was indeed made by the owner of the private key.
The key benefit of digital signatures is that they provide non-repudiation. This means that once a user has signed a message, they can’t later claim that they didn’t make the transaction.
Decentralization: The Network Effect
While cryptography provides a solid foundation for blockchain security, it’s not the only factor at play. Decentralization is another critical component that makes blockchain secure.
In a decentralized network, there’s no single point of failure. Instead, the network is made up of multiple nodes, all working together to validate transactions and maintain the blockchain.
This network effect has several benefits. For one, it makes it much harder for an attacker to launch a successful attack. In a centralized system, an attacker can target a single vulnerable point and gain access to the entire network. In a decentralized system, an attacker would need to compromise multiple nodes, which is much harder to achieve.
Another benefit of decentralization is that it allows for censorship resistance. In a centralized system, a single entity can shut down the network or block certain transactions. In a decentralized system, there’s no single entity that can shut down the network, making it more resistant to censorship.
Consensus Mechanisms: Ensuring Network Agreement
Finally, consensus mechanisms play a critical role in blockchain security. A consensus mechanism is a protocol that allows nodes to agree on the state of the blockchain.
In blockchain, consensus mechanisms are used to validate transactions and ensure that the network is in agreement. The most well-known consensus mechanism is proof-of-work (PoW), which requires nodes to solve complex mathematical equations to validate transactions.
While PoW has been effective in securing the blockchain, it’s not the only consensus mechanism out there. Other mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake (PoS) and delegated PoS (DPoS), have also been developed.
The key benefit of consensus mechanisms is that they allow nodes to agree on the state of the blockchain, without the need for a central authority. This creates a level of trust and security that’s hard to achieve in traditional systems.
Blockchain security is a complex and multifaceted beast. While cryptography provides a solid foundation, it’s just one component of a much larger security ecosystem. Decentralization, digital signatures, and consensus mechanisms all play critical roles in ensuring the security of the blockchain.
Understanding these components is essential for anyone looking to get involved in the world of blockchain. By grasping the underlying principles of blockchain security, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the world of cryptocurrency and decentralized applications.
As the world of blockchain continues to evolve, it’s likely that new security threats will emerge. But with a strong understanding of the underlying components, we’ll be better equipped to adapt and overcome these challenges, creating a safer and more secure blockchain ecosystem for everyone.
