Unveiling The Power Of Zero Knowledge Proofs In Protecting Your Cryptographic Identity
In the world of cryptography, protecting one’s identity is of the utmost importance. With the rise of digital communication, the need for secure and anonymous transactions has become increasingly vital. This is where zero-knowledge proofs come into play – a revolutionary concept that’s changing the game when it comes to safeguarding our cryptographic identities.
- The Future Of Blockchain In Digital Identity Verification
- Revolutionizing Transparency In Governance With Blockchain
- In The World Of Cryptocurrency, Safety Is The Best Investment Strategy
- What Are Crypto Vaults And How Do They Enhance Security
- Unlocking The World Of Crypto Gaming: Your Essential Starter Pack
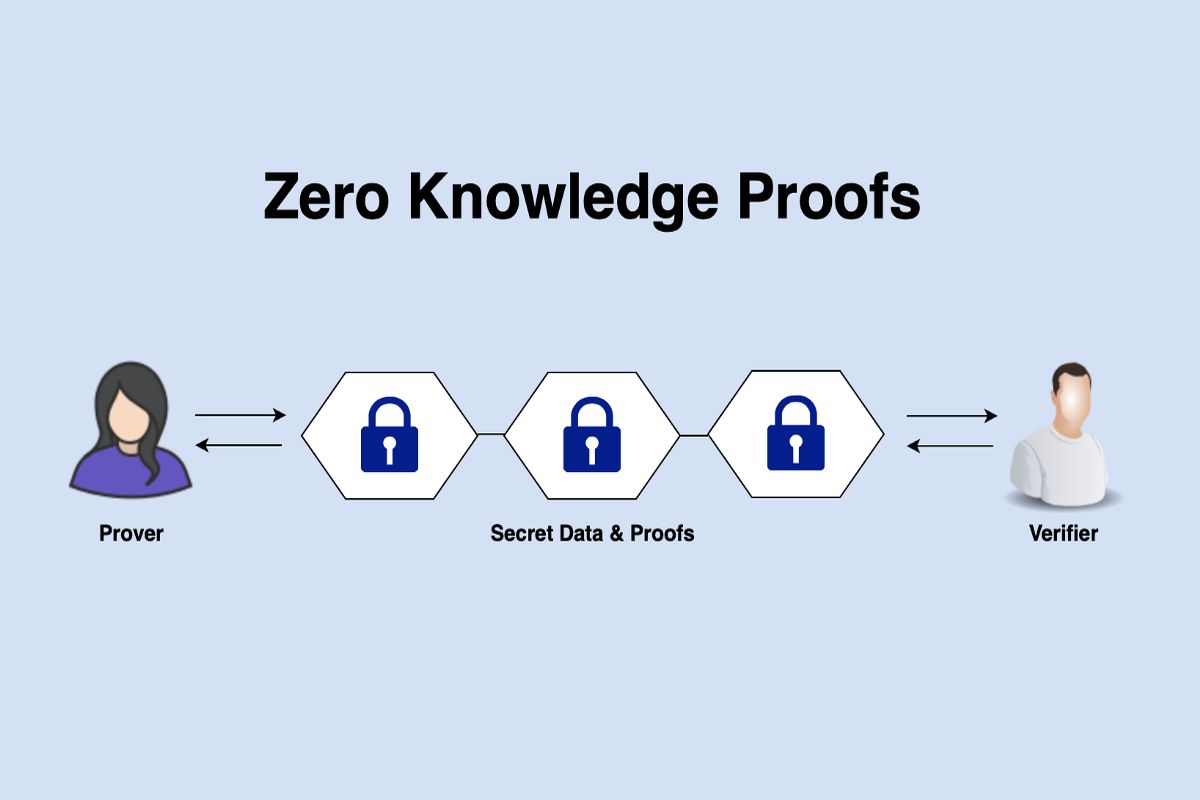
Imagine being able to prove a statement without revealing any underlying information. Sounds like magic, right? But this is exactly what zero-knowledge proofs enable us to do. In essence, they allow us to demonstrate the validity of a claim without disclosing any sensitive data. This is particularly useful in cryptographic contexts, where revealing too much information can compromise our anonymity.
So, how do zero-knowledge proofs work? The concept was first introduced in the 1980s by a group of brilliant cryptographers, including Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff. They proposed a framework that enabled a prover to convince a verifier of a statement without revealing any underlying information. This was achieved through the use of mathematical algorithms and clever encryption techniques.
One of the most significant applications of zero-knowledge proofs is in the realm of authentication. Traditional authentication methods often require users to share sensitive information, such as passwords or identity documents. However, with zero-knowledge proofs, users can prove their identity without revealing any underlying data. This is achieved through a complex dance of encryption and decryption, where the prover demonstrates their identity without actually sharing any information.
Another exciting application of zero-knowledge proofs is in the world of voting systems. Traditional voting systems often require voters to reveal their identity and voting choices. However, with zero-knowledge proofs, voters can prove that they are eligible to vote and that their vote has been cast, without revealing any sensitive information. This enables secure and anonymous voting, ensuring the integrity of the electoral process.
Zero-knowledge proofs also have the potential to revolutionize the world of cryptocurrency. Transactions on blockchain networks are often transparent, meaning that anyone can track the movement of funds. However, with zero-knowledge proofs, users can prove that they have the necessary funds to complete a transaction, without revealing the actual amount or the source of the funds. This enables secure and anonymous transactions, protecting users’ identities and financial information.
In conclusion, zero-knowledge proofs are a powerful tool in the world of cryptography, enabling us to prove statements without revealing any underlying information. This has far-reaching implications for authentication, voting systems, and cryptocurrency transactions. As the world becomes increasingly digital, the need for secure and anonymous communication will only continue to grow. And with zero-knowledge proofs, we can rest assured that our cryptographic identities will remain protected.
In a world where data is the new currency, zero-knowledge proofs are a breath of fresh air. They offer a beacon of hope for those seeking to protect their anonymity and maintain control over their sensitive information. As we move forward in this digital age, it’s essential that we continue to develop and refine zero-knowledge proofs, ensuring that our cryptographic identities remain secure and protected.
So, the next time you hear about zero-knowledge proofs, remember that they’re not just a fancy cryptographic concept – they’re a powerful tool that’s changing the game when it comes to protecting our identities and safeguarding our sensitive information.
