What Are Decentralized Autonomous Organizations Daos
Imagine a world where organizations are run not by a single person or a small group of people, but by a collective, where decisions are made through a consensus-driven process, and where everyone has a say in how things are run. Sounds like a utopia, right? Well, this world is not as far-fetched as you might think, thanks to the emergence of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, or DAOs.
- A Collaborative Approach To Crypto Staking
- Navigating The World Of Blockchain: Unlocking The Potential Of Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
- A New Era In Healthcare: How Blockchain Is Revolutionizing Medical Data Management
- Embracing The Future Of Payments: A Step-by-Step Guide To Setting Up A Crypto Payment Processor For Your Business
- Navigating The Turbulent World Of Crypto Trading: A Deep Dive For Seasoned Enthusiasts
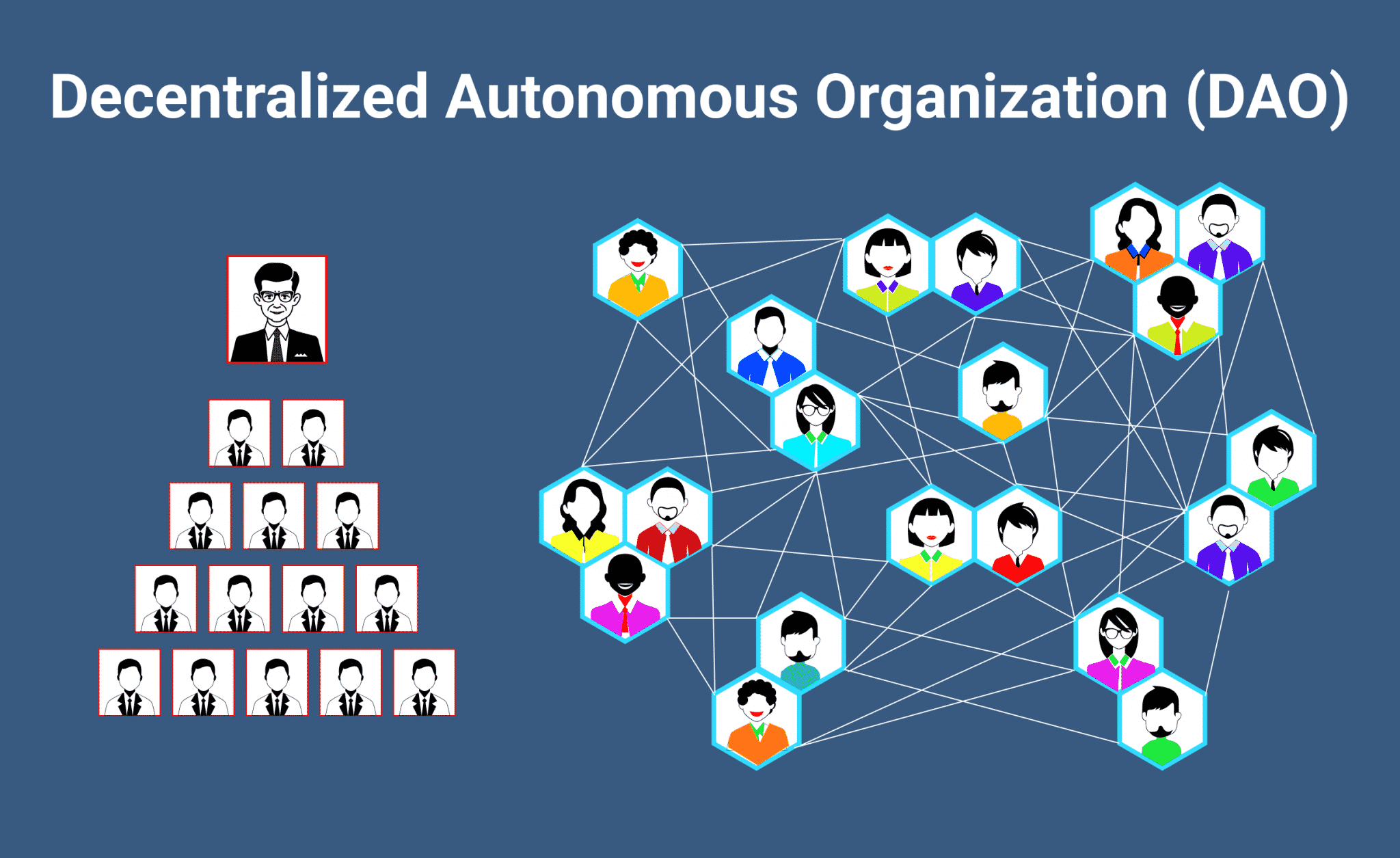
So, what exactly is a DAO? In simple terms, a DAO is a digital organization that operates on a blockchain, a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions and data. But what sets DAOs apart from traditional organizations is that they’re not controlled by a single entity. Instead, they’re governed by a set of rules encoded in smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into lines of code.
This means that DAOs are not beholden to any single person or group. Decisions are made through a consensus-driven process, where members of the DAO vote on proposals and changes to the organization. This creates a transparent, decentralized, and community-driven decision-making process that’s resistant to censorship and tampering.
But how do DAOs work in practice? Let’s take a look at a few examples. One of the earliest and most well-known DAOs is The DAO, which was launched in 2016 on the Ethereum blockchain. The DAO was a venture capital fund that allowed members to invest in startups and projects, with decisions made through a voting process.
Another example is MakerDAO, which is a decentralized lending platform that allows users to borrow a stablecoin called DAI. The interest rates and other parameters of the platform are set through a voting process, where members of the DAO decide how the platform should operate.
DAOs have a number of benefits over traditional organizations. For one, they’re much more transparent and accountable. Because all decisions and transactions are recorded on a blockchain, anyone can see how the organization is operating and make decisions based on that information.
DAOs are also much more resilient to censorship and tampering. Because they’re not controlled by a single entity, it’s much harder for governments or other actors to shut them down. And because decisions are made through a voting process, members of the DAO have a much greater degree of control over how the organization is run.
But DAOs aren’t without their challenges. One of the biggest hurdles they face is regulatory uncertainty. Because DAOs are still a relatively new phenomenon, there’s a lot of uncertainty around how they should be regulated. This can make it difficult for DAOs to operate in certain jurisdictions, and can also make it hard for them to attract investment and talent.
Another challenge DAOs face is scalability. Because they’re built on blockchain technology, they can be slower and more cumbersome than traditional organizations. This can make it difficult for them to operate at scale, and can also make it hard for them to compete with traditional organizations.
Despite these challenges, DAOs have the potential to fundamentally change the way we think about organizations and governance. By providing a transparent, decentralized, and community-driven decision-making process, DAOs offer a new model for how organizations should be run.
And as the technology continues to evolve and mature, we’re likely to see more and more DAOs emerge in a wide range of industries and sectors. From finance to healthcare to education, DAOs have the potential to disrupt traditional business models and create new opportunities for innovation and growth.
So what does the future hold for DAOs? Only time will tell, but one thing is certain: DAOs are here to stay, and they’re likely to play a major role in shaping the future of organizations and governance.
